How to design mediated touch experiences in
affective communication for remote loved ones?
Keywords:
Mediated social touch, Social Connection
Asynchronous communication,
Auto-ethnographical design method
Year:
2021-2022, Individual Project
Professors:
Angelika Mader, Edwin Dertien, Jelle van Dijk
Role:
HCI Researcher, Designer, Developer
2021-2022, Individual Project
Professors:
Angelika Mader, Edwin Dertien, Jelle van Dijk
Role:
HCI Researcher, Designer, Developer
About:
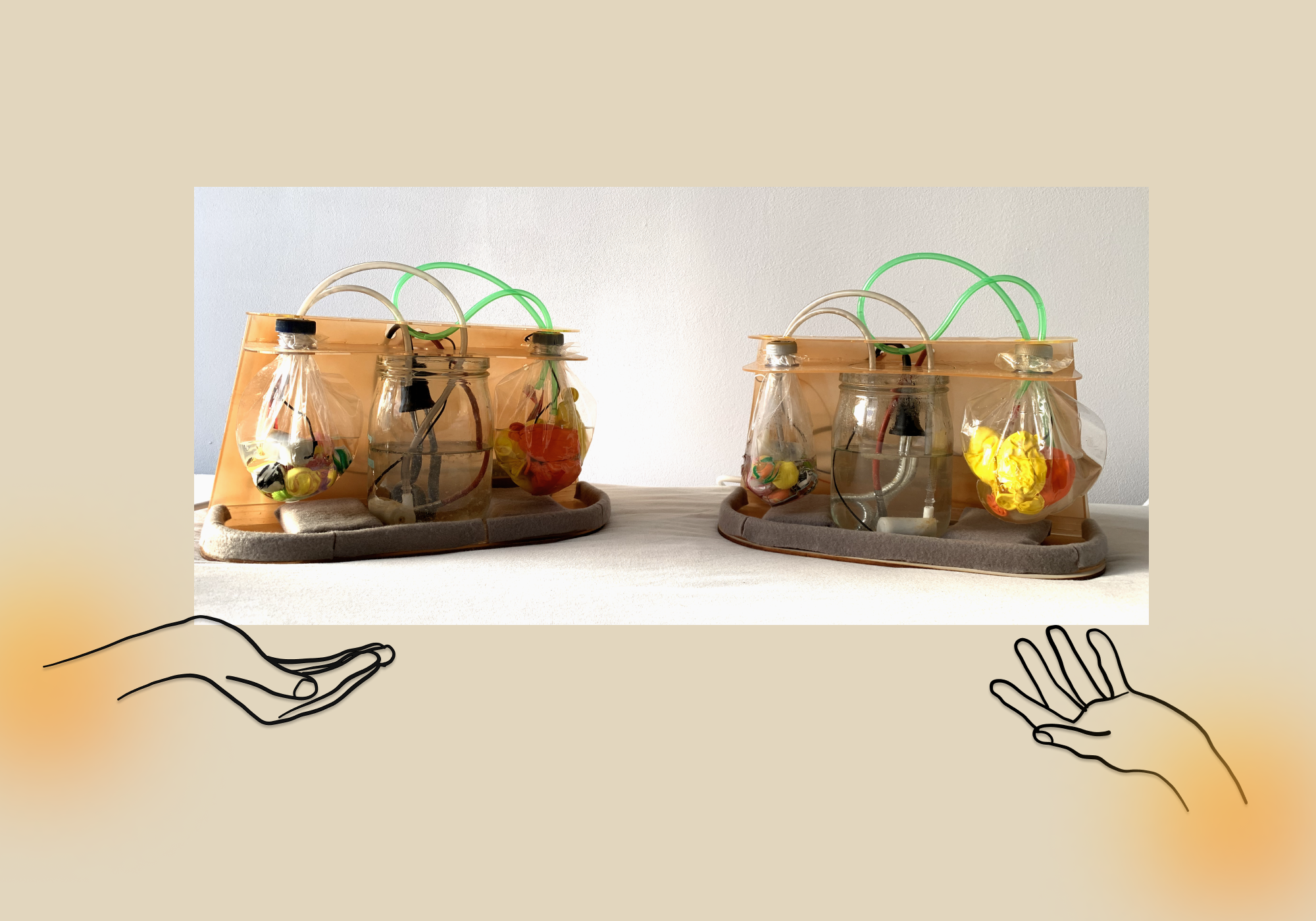
Telesense is a HCI research about mediated social technology for remote lovers. I created a pair of communication devices that enable users to communicate in distance by applying touch sensation with warmth and vibration, to enhance the feelings of connection in mediated affective communication. Besides focusing on non-real time channels, where the touch message can be stored on the device, this touch communication tool studied the meaning and impact of asynchronicity in affective communication.
Highlight:
![]()
Telesense is a HCI research about mediated social technology for remote lovers. I created a pair of communication devices that enable users to communicate in distance by applying touch sensation with warmth and vibration, to enhance the feelings of connection in mediated affective communication. Besides focusing on non-real time channels, where the touch message can be stored on the device, this touch communication tool studied the meaning and impact of asynchronicity in affective communication.
Highlight:
- Touch sensation exploration: warmth in soft tactile materials ︎︎︎
- Asynchronous communication resolve the social pressure in online communication︎︎︎
- Screen is gone & Ambiguous information for affective communication︎︎︎
- Combine auto-ethnographic design method and user study with daily logbook︎︎︎
- Creative technology design progress: tinker with design︎︎︎

Introduction
Background
︎Touch deviation under the social-distancing context;
︎Touch sensation is missing in communication channels for remote lovers;
︎Look for soft and less machine-like touch sensation given by mediated touch technology
︎Touch sensation is missing in communication channels for remote lovers;
︎Look for soft and less machine-like touch sensation given by mediated touch technology
Research Question
︎How can a mediated social touch technology with the asynchronous channel enhance social connectedness for remote loved ones?
︎︎︎Research Journey
Observe & Understand
This phase is to observe and understand the behavior of communication on instant message tools for remote loved ones. Focus on immediacy of communication, the results helped to define the problems and look for design opportunites of synchronous/asynchronous communication for loved ones.
Method:
︎Diary Study
︎Semi-structured interviews
Participation:
︎Diary Study
︎Semi-structured interviews
Participation:
- Myself, as the real user, has been observed first
- 3 individual participants and 3 pair participants joined the study
- Logbook for daily online communication with one close friend/partner, 3~5 days
Focus points:
- Behavior and feelings of immediate/asynchronous response
- Behavior and feelings of starting/ending conversation
- Comparison of feelings for text/ audio/video-based channel
- Relation between self, phone and remote partner
Selected quotes from user research︎︎︎
︎ Key Takeaways
01. Users have the common sense that messages are expected to respond promptly under the social norm
02. Partial presence in the mediated communication could result the feeling of disconnection for the others
03. The asynchronous could generate the guilt but may create the spark of connection
04. Notification > messages, as a signal of affection
05. Video-based channel may cause strong feelings of separation after it ends
06. Communication tool could be the presence of the remote lover
01. Users have the common sense that messages are expected to respond promptly under the social norm
02. Partial presence in the mediated communication could result the feeling of disconnection for the others
03. The asynchronous could generate the guilt but may create the spark of connection
04. Notification > messages, as a signal of affection
05. Video-based channel may cause strong feelings of separation after it ends
06. Communication tool could be the presence of the remote lover
Define: carving out the design directions
︎Communication Experience
- Focus on asynchronous channel to support affective communication
- Resolve the social pressure generated by expectations of immediate responseProvide the calm and pleasant communication experience
- Enhance the feeling of connection
︎Touch Experience
- Implement soft tactile sensation into the mediated touch technology
- Reduce intrusiveness from mediated touch
- Reduce the visual workload in the mediated communication
- Provide ambiguous but understandable information from touch message
︎︎︎System overview
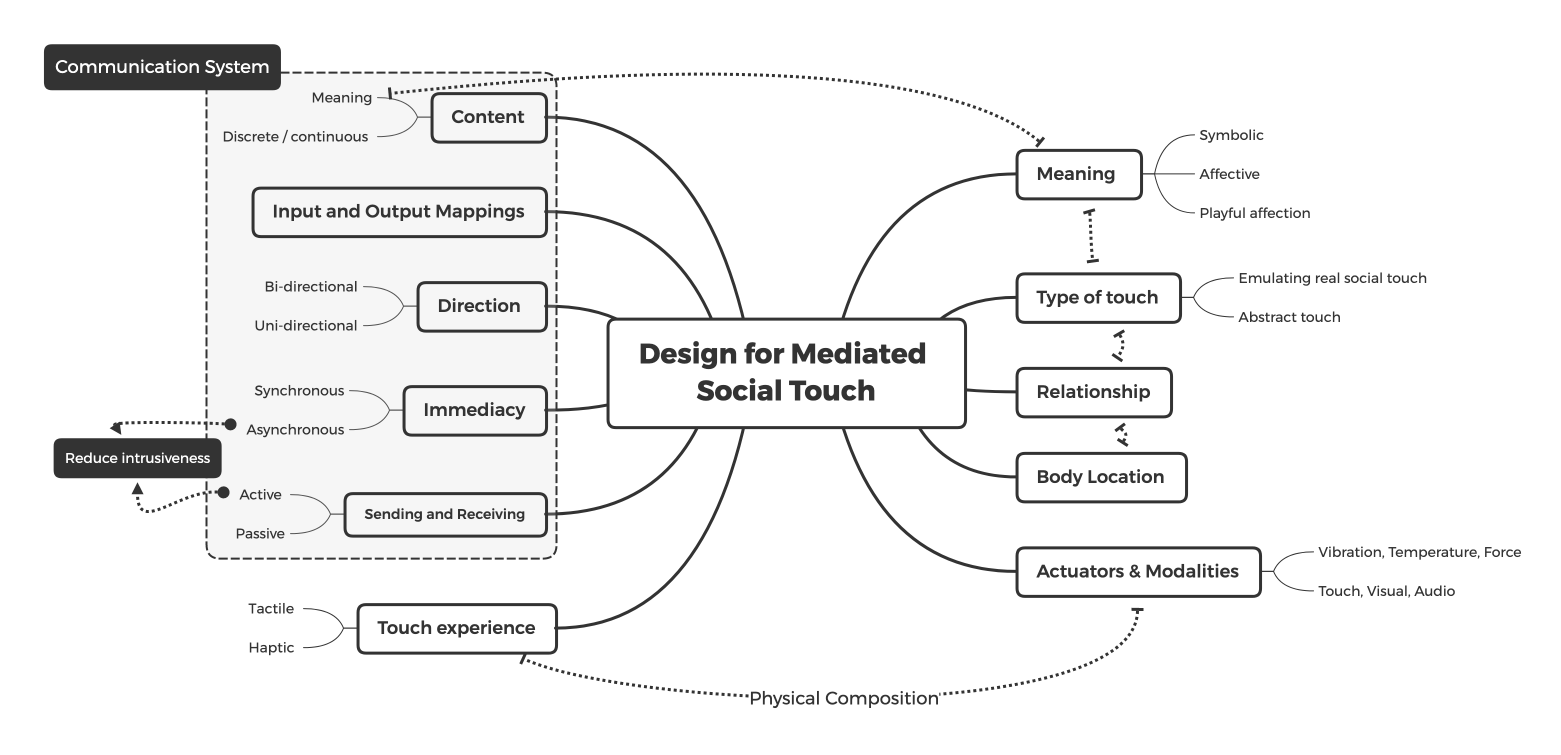
、
Design & Make
Cycle 1
Create a Usable Communication System
This cycle generated the initial system concept and created first prototype for lab-test. The results helped for second development cycle. To kick-off the design process, a moodboard helped me get ideas to establish the concept of communication system, and also to explore the materials affording the tactile sensation.
︎︎︎Moodboard
![]()
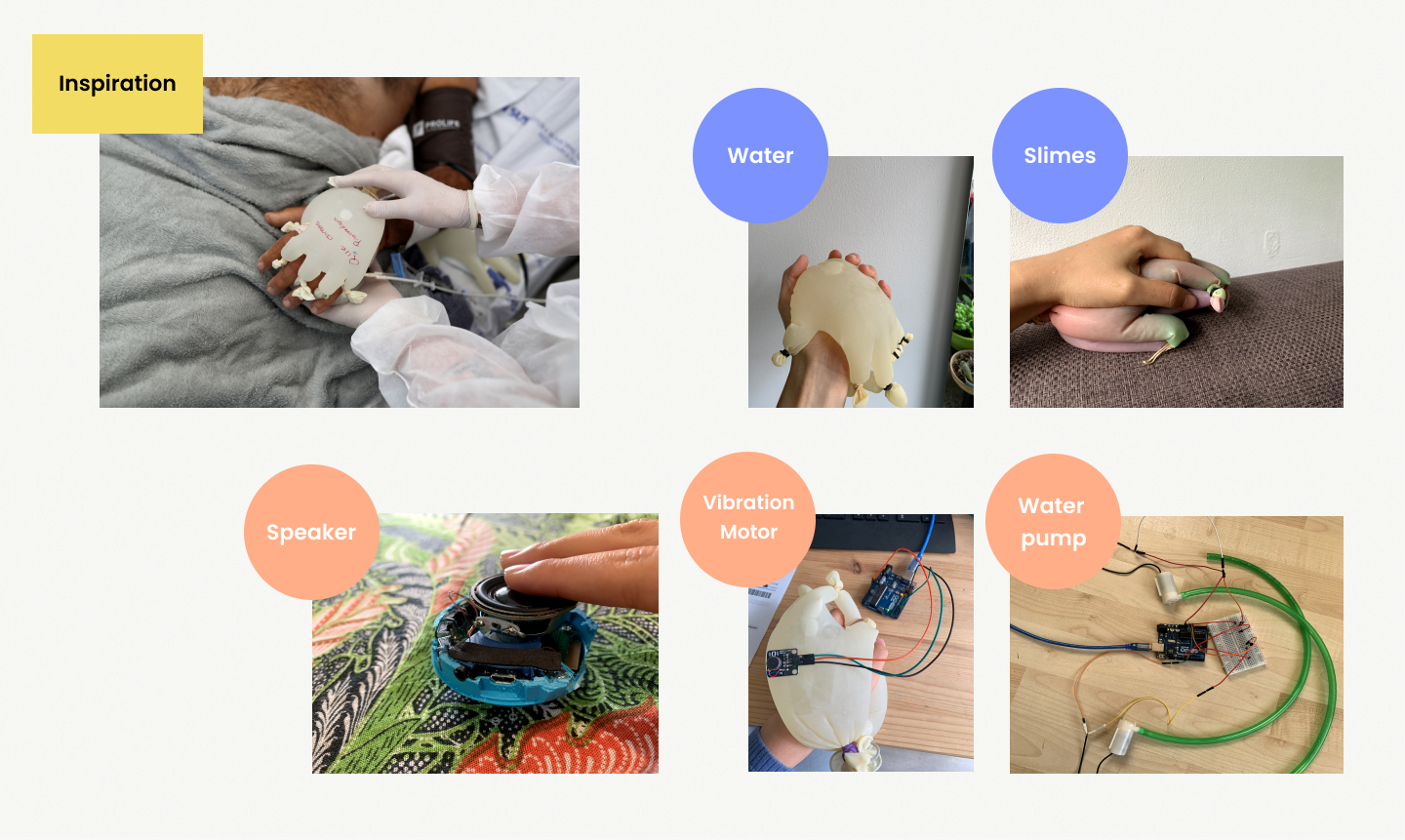
Specalisation Exploration
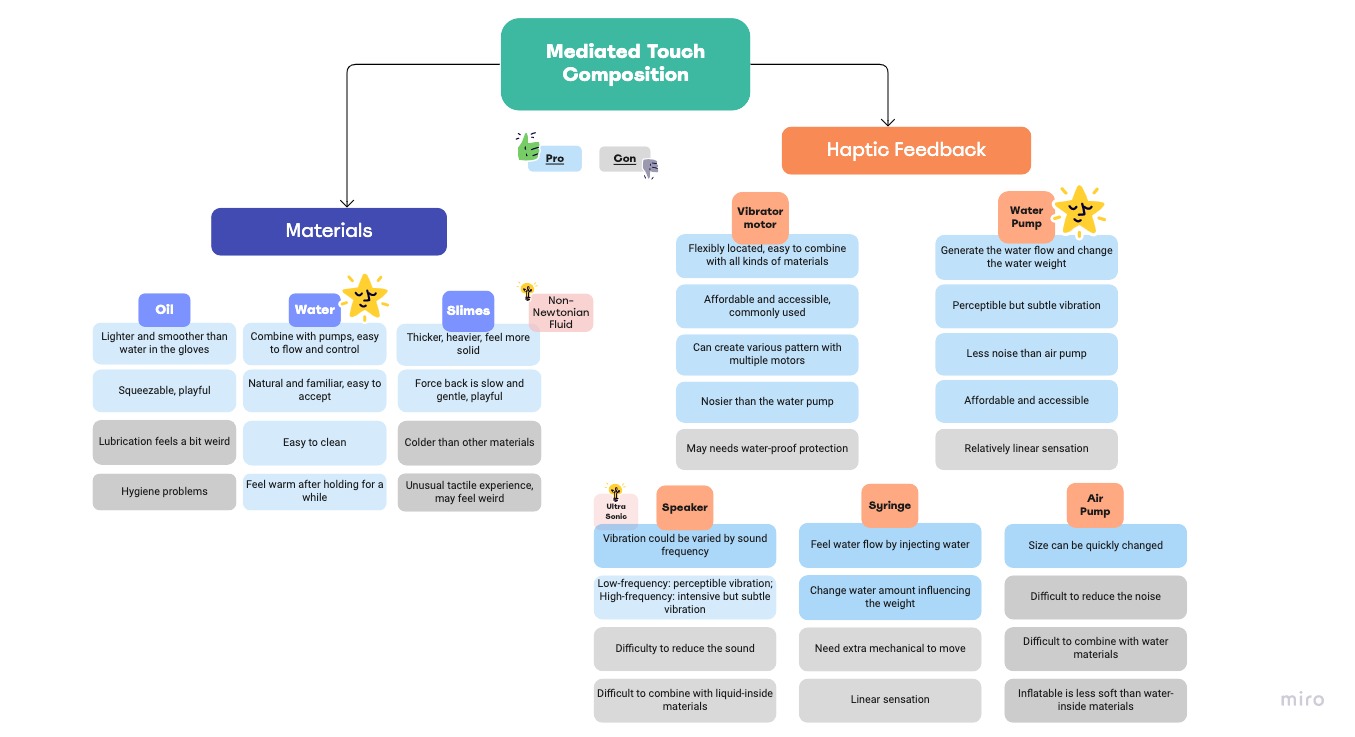
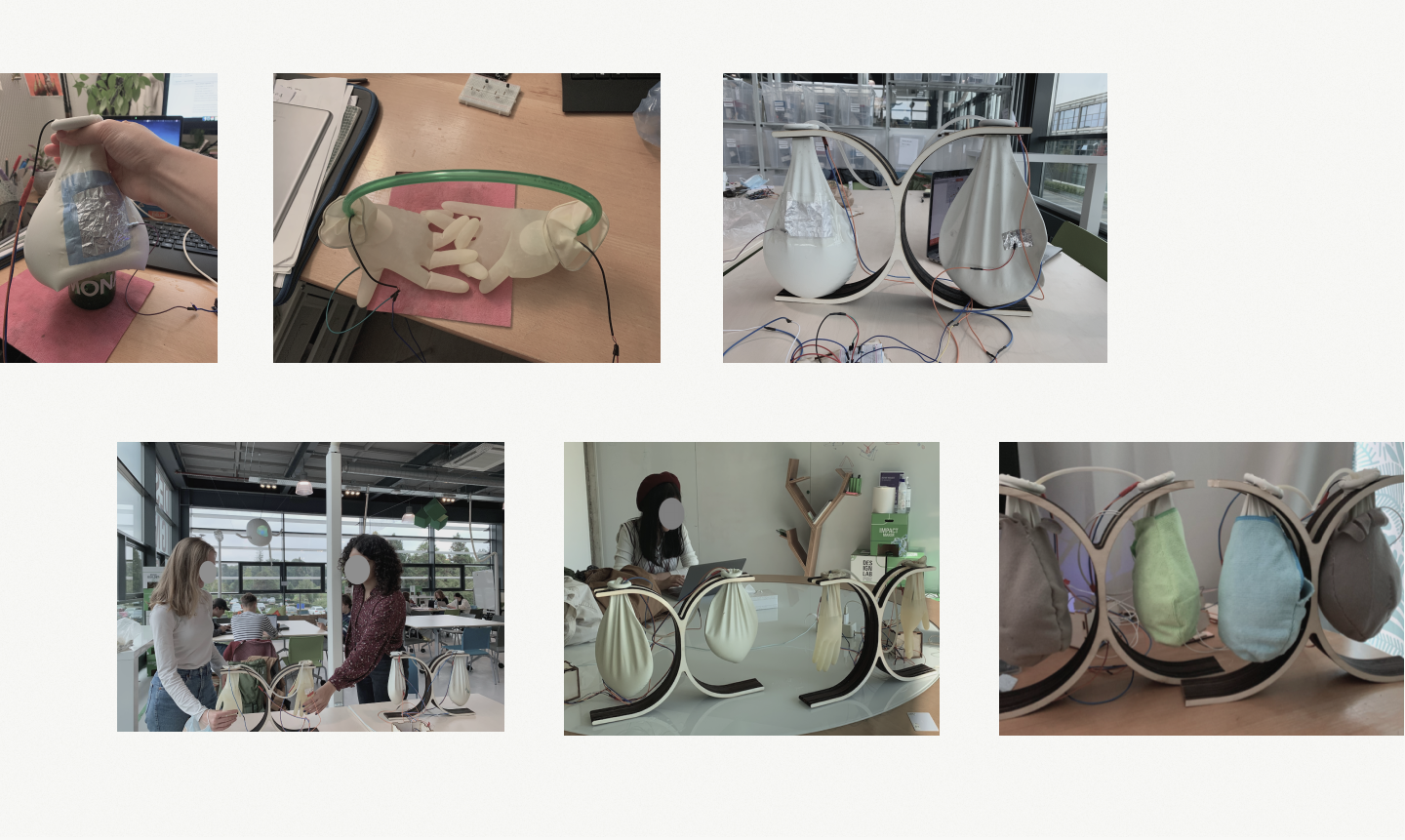
Brazilian hospital have used latex gloves with filling warm water to mimic human touch to help patients against isolation during pandemic. With this inspiration, I filled different materials into gloves to experience the tactile affordance, including water, oil, and slimes. Based on the soft materials, I explored a few actuators: vibration motors, water pump, speaker, syringe, air pump. Pros&cons of materials and haptic feedback were listed after experiments
︎ Key Takeaways
01. The water pump with water gloves were chosen for further development
02. Water pump provided the subtle vibration with little noise
03. Slimes afford both solid and fluid touch sensation, but cold and may gives strange feelings
01. The water pump with water gloves were chosen for further development
02. Water pump provided the subtle vibration with little noise
03. Slimes afford both solid and fluid touch sensation, but cold and may gives strange feelings
Experiments︎︎︎
Pros&Cons︎︎︎
System Concept
A symmetric system was formed initially. Each user has two ports to send and receive touch respectively: sending and receiving port. For the touch input, the remote device will act in the same way to the activated one. This system supports both real-time channel and asynchronous channel for touch communication.
Symmetric System︎︎︎

Real-time Channel︎︎︎
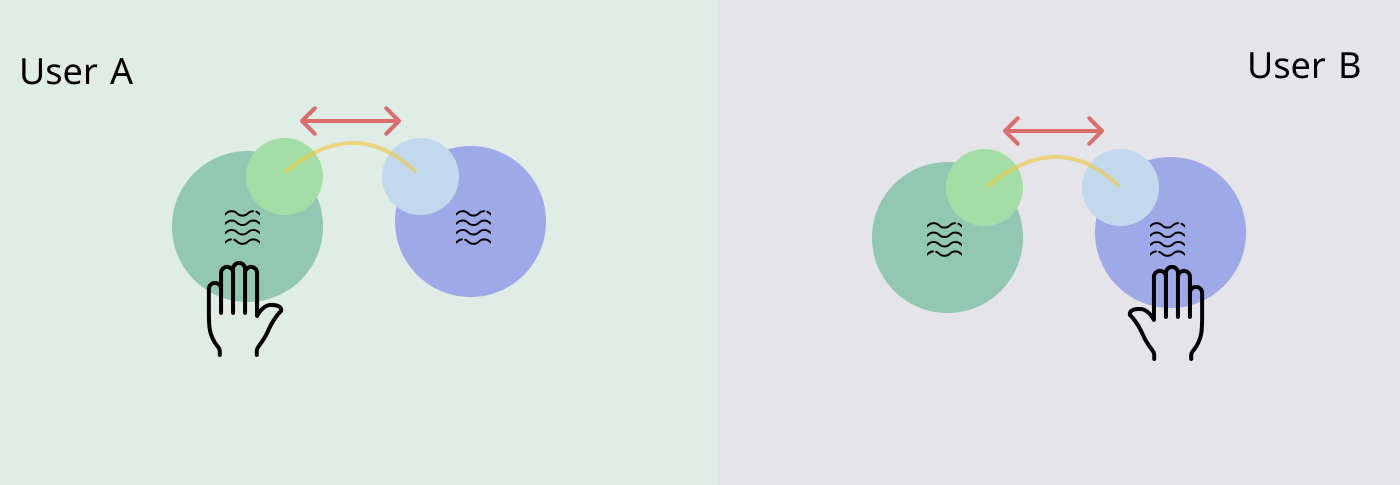
Asynchronous Channel︎︎︎

Realisation & Evaluation
Formed by two water pumps, touch sensor made by aluminium foil, physical communication system was completed. The lab-test was conducted to evaluate usability. Pairs of participants tried out the devices, collecting user feedback by interview and survey. After lab-test, a test in real life setting was conducted for a few days between me and my friend. The results helped to improve the communication system in the Design and Make Cycle II.
︎︎︎Experiments & Lab-test
![]()

︎ Key Takeaways
01. Warmth are expected with water
02. Weight change was too subtle to feel
03. For real-time communication, the vibration is given both by sending and receiving actions, which is confusing
04. Real-time was more attractive in the lab, asynchronous communication was ignored
05. Physical form needs to be improved to be robust
06. Symmetric sending and receiving ports are hard to distinguished
01. Warmth are expected with water
02. Weight change was too subtle to feel
03. For real-time communication, the vibration is given both by sending and receiving actions, which is confusing
04. Real-time was more attractive in the lab, asynchronous communication was ignored
05. Physical form needs to be improved to be robust
06. Symmetric sending and receiving ports are hard to distinguished
Design & Make
Cycle 2
A focus on information simplicity and warmth
Considering the users' feedback, this cycle improved the prototype focusing on three aspects: warmth on the devices, robust physical form, minimised visual information. Final evaluation were conducted in the participants' home and lasted for a few days. In the end, design knowledge and reflection for future study are given.
Supply warmth
A water camping heater was applied to warm the water. Due to safe concern, the water level should be in the fixed amount, so water only flow between heating port and receiving port. Therefore, only receiving action could sense the warmth.
︎︎︎Devices illustration
![]()
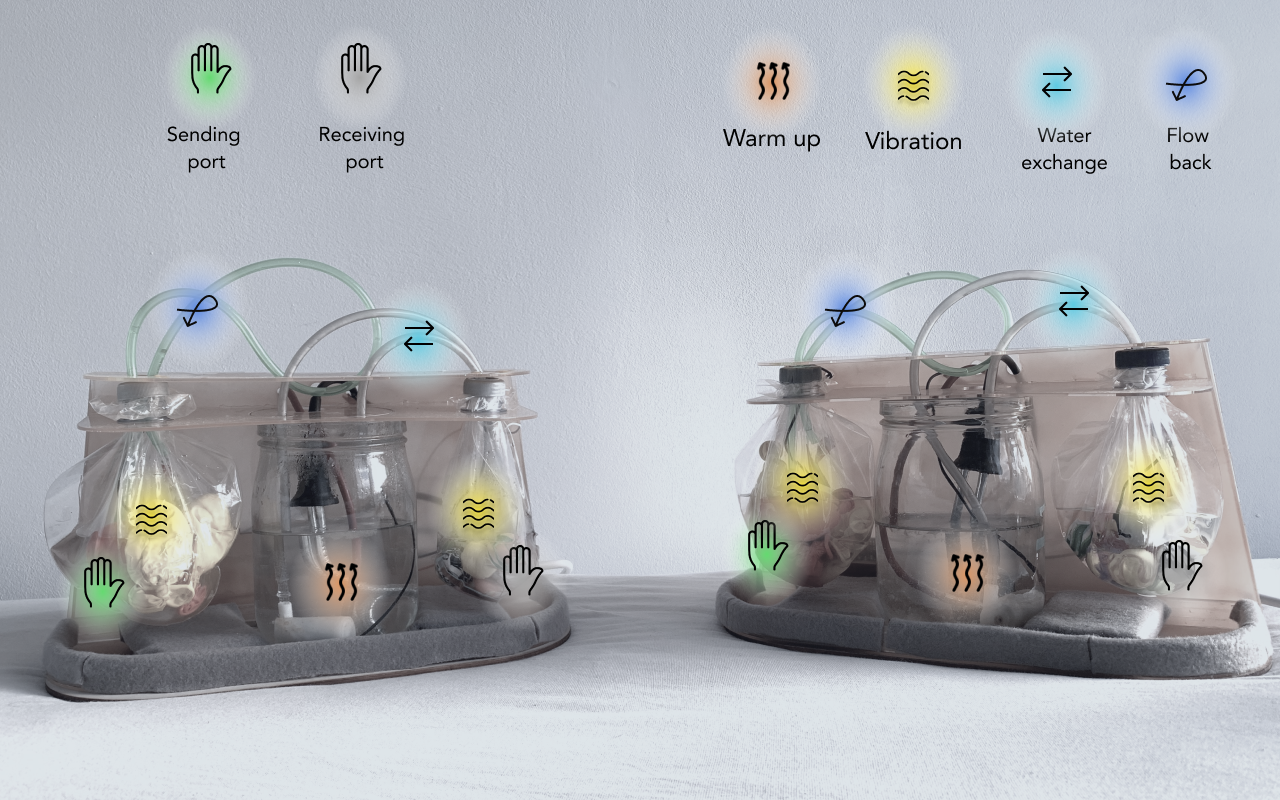

Clear and minimised information
Visual notification is removed. Users only know whether there is a message by touching the device. The information is primarily conveyed by the touch sensation rather than visualisation, users could close eyes to use the devices
Real-time and asynchronous communication
- Messages are formed by touching duration,
- Messages are stored by adding up duration
- Warmth could be remained until the user receive
- Users could send and receive at same time
Evaluation
5 pairs of participants (3 pairs of friends, 2 pairs of couples) joined for the in-life evaluation. Prototype were set up at their own places, and they used it as a communication tool for 3~5 days with writing a daily logbook. After in-life test, a survey for usability and interview for open discussion were conducted.
︎︎︎Results from the survey
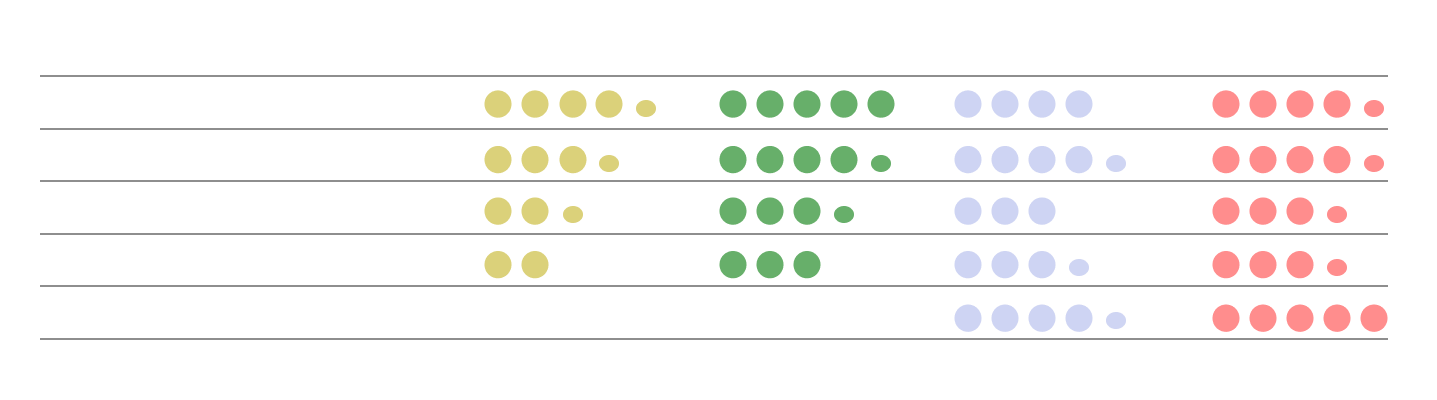
︎ Key Takeaways
01. A pleasant experience was given
02. This channel improved the communication quality
03. Given experiences seems more impactful on feelings of "we are connected"
04. Asynchronous channel has effect on feelings of "we are together" more than touch communication
05.Sending and receiving both felt pleasant, receiving seems more impactful on feelings
︎︎︎Logbook and interview results
︎ Key Takeaways
01. Resolve the disappointment from no messages when receiving
02.Combine other modalities: audio, visual
03. Richer information in message, various pattern of vibration
04. One-to-one VS. one-to-multiple users
05. Portable size and durable affordance
06. Soft materials with muted colour
01. Resolve the disappointment from no messages when receiving
02.Combine other modalities: audio, visual
03. Richer information in message, various pattern of vibration
04. One-to-one VS. one-to-multiple users
05. Portable size and durable affordance
06. Soft materials with muted colour
Conclusion: Design knowledge for future study
︎Design for mediated touch communication
-
Soft and warm fluid is comprising application for mediated affective communication
-
Active touch could reduce the intrusiveness
-
Touch and being touched both could generate pleasantness
-
Ambiguous information could enhance communication experiences
-
Mediated touch may be open for various relationships under the unintimate design
︎Design for asynchronous communication
-
With time gap of communication, interaction should be able to be picked up
-
Real-time channel is supposed to remain in asynchronous channel
-
Touch and being touched both could generate pleasantness
-
Mediated touch may be open for various relationships under the unintimate design
Discussion
Affection in ambiguity: Screen is gone, Time is unknown
In this communication channel, communication is situated in an ambiguous context for people in close relationship but live apart. The ambiguity is created by abstract meanings in touch message, and unknown time points from asynchronous channel. Besides, instead of reading but touching to communicate, information is transferred from visible to perceptible, creating a context that screen, which affords the massive visible information, is gone. Which is a meaningful topic for discussion in this age where the communication technology is pervasive, I proposed a few open questions below.
︎
Open questions
︎Reflection on research Journey
- How to apply ambiguity to enhance the affection for remote lovers in mediated communication?
-
What will be meaningful mediated communication for remote lover?
-
How to design a meaningful communication experience for remote lovers?
-
What will be meaningful information given by mediated communication tools?
- When the digital device plays the presence of the remote lover, how to design the affective mediated communication experience to build a healthy human-technology relation?
︎Reflection on research Journey
- First person perspective helps with understanding and defining the real problems, digging out the problems which are hard to reveal in the massive user research
-
Self-observation requires continuous documenting, the tool to help self-observation for HCI researcher could be developed in the future study
-
Self-observation also needs the interaction with others, inviting users are necessary for auto-ethnographic design method
-
Putting self in the HCI researcher, helps to reflect on the relation of technology and human
-
Tinkering helps with thinking in the designing process to form a pragmatic solution
︎Closing words
Technology is the best when
it brings people together,
it brings people together,
to and in,
the physical world.
the physical world.
